
Best Hair Loss Treatment for Male
- Best Hair Loss Treatment for Male
- Hair Loss Treatment Options
- Pharmaceutical Approaches
- Combination Therapy
- Surgical Interventions
- Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
- Best Course of Action
- Hair Loss Treatment for Men
- Merits of PRP for Hair Loss
- Limitations of PRP for Hair Loss
- Clinical Guidelines and Safety Measures
- Patient Selection Criteria
- Contraindications
- Future Directions
Best Hair Loss Treatment for Male
Male pattern baldness, medically referred to as androgenetic alopecia, affects millions worldwide, accounting for over 95% of hair loss cases in men. Characterised by receding hairlines and thinning crowns, this hereditary condition arises from the interaction of genetics, hormones, and aging. Fortunately, advancements in modern medicine have yielded a plethora of treatment options, empowering men to combat hair loss and restore confidence. This article explores the best hair loss treatments for males, focusing on both pharmaceutical and surgical approaches, along with lifestyle modifications and home remedies.
Hair Loss Treatment Options
- PRP Hair Treatment: Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): FUT Hair Transplant Procedure
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): FUE Hair Transplant Procedure
- Essential Oils: Infusing Carrier Oils with Rosemary, Peppermint, Lavender, or Cedarwood
- Finasteride Hair Loss Tablets: Sold Under the Brand Names Proscar and Propecia
- Minoxidil Topical: Can Help Hair Regrowth
- Derma Roller 1.5mm: Hair Regrowth Micro Needles
Pharmaceutical Approaches
Two primary classes of drugs constitute approved pharmaceutical interventions for male pattern baldness:
Minoxidil
Marketed under brand names such as Rogaine®, minoxidil is a topical solution applied directly onto the scalp. Initially developed as an oral vasodilator, researchers discovered its propensity to stimulate hair growth as a serendipitous side effect. Mechanistically, minoxidil prolongs the anagen phase of the hair cycle, thereby increasing follicle size and density. Noteworthy advantages comprise ease of application, affordability, and negligible systemic absorption. Adverse events may include irritant contact dermatitis, hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth beyond intended sites), and hypotension (low blood pressure).
Finasteride
Finasteride, sold under brands like Propecia® and Proscar®, functions as a Type II 5α-reductase inhibitor, impeding testosterone conversion into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the primary culprit implicated in male pattern baldness. Oral consumption of finasteride reduces circulating DHT levels by approximately 70%, subsequently halting progression of hair loss and fostering partial regrowth. Advantages encompass once-daily dosage, relatively affordable price point, and demonstrated efficacy in slowing hair loss and promoting regrowth. Potential adverse effects consist of decreased libido, ejaculatory dysfunction, gynecomastia (breast development in men), and elevated risk of prostate cancer.
Combination Therapy
Integrating both minoxidil and finasteride yields superior outcomes compared to monotherapy, attributable to synergistic interactions between these compounds. According to a study published in the Journal of American Academy of Dermatology, concurrent usage led to enhanced hair count gains relative to standalone treatments. Despite increased expenses and potential side effects, combination therapy provides a compelling approach for optimizing hair restoration efforts.
Surgical Interventions
When pharmaceutical options prove insufficient, surgical procedures emerge as viable alternatives, namely:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Also known as strip harvesting, FUT entails excision of a linear ellipse of donor-dominant scalp from the posterior occipital region, followed by segmentation into individual follicular units for subsequent implantation. Resultant scarring assumes a barely perceptible straight line concealed beneath adjacent hair tufts. Suitable candidates exhibit adequate donor supply and stable recipient zones devoid of progressive miniaturization.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
An evolution of earlier punch graft techniques, FUE harvests individual follicular units directly from the donor zone utilizing automated devices or manually wielded punches. Comparatively, FUE engenders minimally detectable circular scars scattered randomly across the harvest site, obviating the requirement for suture closure. Candidates must possess sufficient donor reserves and meet predetermined criteria for selection.
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
Complementing pharmaceutical and surgical strategies, lifestyle adjustments and holistic remedies fortify overall hair health, including:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming nutrient-dense foods rich in proteins, vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids strengthens hair shaft integrity and encourages healthy growth cycles.
- Scalp Massage: Regularly massaging the scalp stimulates circulation, delivering oxygen-rich blood flow to hair follicles, thus promoting thickening and densification.
- Essential Oils: Infusing carrier oils with rosemary, peppermint, lavender, or cedarwood extracts purportedly invigorates hair growth and slows shedding. However, rigorous scientific validation remains pending.
- Saw Palmetto: Derived from the fruit of Serenoa repens, saw palmetto allegedly suppresses 5α-reductase activity, mirroring finasteride’s mechanism of action. Limited evidence corroborates its efficacy, mandating cautious interpretation.
Best Course of Action
Navigating the multitude of hair loss treatments available demands careful consideration of individual circumstances, medical history, and personal preferences. Engaging in honest discourse with healthcare professionals enables informed decision-making, ultimately leading to satisfactory outcomes. Embracing a holistic approach combining pharmaceuticals, surgical interventions, lifestyle adaptations, and adjunctive therapies maximizes the potential for reversing hair loss and preserving a full, vibrant mane.
Hair Loss Treatment for Men
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has recently emerged as a promising treatment modality for male pattern baldness, capitalising on the regenerative prowess of autologous platelets. This innovative approach entails drawing a patient’s blood, subjecting it to centrifugation to isolate platelet-rich plasma, and subsequently reinjecting the concentrated suspension into affected scalp regions.
The rationale underpinning PRP for hair loss revolves around the abundant growth factors encapsulated within platelets, notably platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF). Collectively, these molecules instigate cascades of molecular signalling, inciting angiogenesis, stem cell recruitment, and extracellular matrix remodelling, consequently triggering dormant follicles to transition from telogen (resting) to anagen (growth) phases. Herein, we shall expound upon the merits, practicalities, and limitations of PRP therapy as a viable hair loss treatment option for men grappling with androgenetic alopecia.
Merits of PRP for Hair Loss
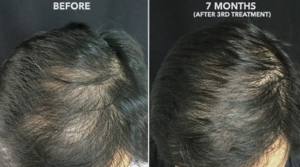
Autologous Nature
Since PRP originates from the patient’s own blood, ethical concerns pertaining to sourcing exogenous materials are circumvented, coupled with vanishingly remote risks of immunogenicity or infectious transmissions.
Minimally Invasive
Compared to surgical interventions such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE), PRP therapy constitutes a comparatively nontraumatic endeavour, eschewing lengthy recoveries and attendant morbidities.
Tailored Treatment
Given the idiosyncrasies inherent in each individual’s constitution, PRP therapy lends itself to bespoke formulations, permitting tailored optimisation of growth factor cocktails according to unique pathophysiological profiles.
Limitations of PRP for Hair Loss
Variability in Preparation Techniques
Standardisation of PRP procurement remains elusive amidst a heterogeneous landscape of commercially available kits, confounding attempts to establish universally applicable protocols and benchmarks.
Scarcity of High-Quality Evidence
Robust randomized controlled trials validating PRP’s putative benefits vis-à-vis conventional hair loss treatments remain wanting, leaving residual uncertainty concerning its comparative efficacy.
Short Half-Life
Endogenous platelets exhibit finite functional longevity, estimated at approximately seven to ten days, implying that repeated injections may be requisite to maintain sustained therapeutic benefit.
Clinical Guidelines and Safety Measures
Optimal outcomes rely crucially on adherence to recommended clinical guidelines and safety precautions, summarized below:
- Prioritize venesection from antecubital fossae, avoiding superficial veins susceptible to collapse and hematoma formation.
- Utilize double syringe technique to minimize platelet activation and premature growth factor release.
- Opt for dual spin protocols employing hard-spin and soft-spin cycles to achieve optimal platelet concentration without compromising fibrin architecture.
- Thoroughly irrigate and cleanse recipient sites, eradicating debris and sebum that could otherwise impede efficient platelet deposition.
- Avoid undue force during injection, mitigating iatrogenic trauma and unwarranted intravasation.
Patient Selection Criteria
Meticulous patient screening ensures judicious allocation of resources and tempered expectations. Appropriate candidates fulfil the following criteria:
- Age > 18 years
- Diagnosed exclusively with androgenetic alopecia (Norwood Hamilton Classification Stage I-IV)
- Possess intact hair follicles (< 50% Miniaturization)
- Exhibit negative family history of discoid lupus erythematosus, diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, and hemodynamic instability
- Devoid of chronic liver disease, hypofibrinogenemia, coagulopathies, or current anticoagulation therapy
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications preclude initiation of PRP therapy altogether, whereas relative contraindications dictate heightened vigilance and discretionary judgment calls.
Absolute Contraindications
- Chronic liver disease
- Hemodynamic instability
- Sepsis
- Active chemotherapeutic regimen
Relative Contraindications
- Smoking
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Illicit drug abuse
- Systemic corticosteroids
- Antiplatelet agents (Aspirin, Clopidogrel)
Future Directions
Expedited advances in nanotechnology, biomedical engineering, and gene editing promise to revolutionise PRP therapy, ushering forth next generation innovations poised to overcome extant shortcomings and unlock unprecedented potential. Amongst envisioned developments are:
- Engineered platelets bearing targeted fusion proteins capable of homing onto specified cell types or extracellular matrices
- Synthetic analogues mimicking native growth factor structure-activity relationships devoid of immunogenicity concerns
- Genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells programmed to express designated trophic factors in response to environmental cues
In summary, PRP therapy holds immense promise as a hair loss treatment option for men afflicted by androgenetic alopecia, hinging on its auspicious blend of autologous composition, minimal invasiveness, and customizable delivery. Rigorous compliance with clinical guidelines and judicious patient selection optimize chances of success, whilst ongoing technological breakthroughs portend exciting horizons ahead.
Can You Get PRP Injections on the NHS
2 Comments
Best 3 Month PRP for Hair Loss Before and After – PRP Finder
[…] Best Hair Loss Treatment for Male […]
March 18, 2024

Complete Guide to PRP Treatment UK – Best PRP Finder
[…] Best Hair Loss Treatment for Male […]